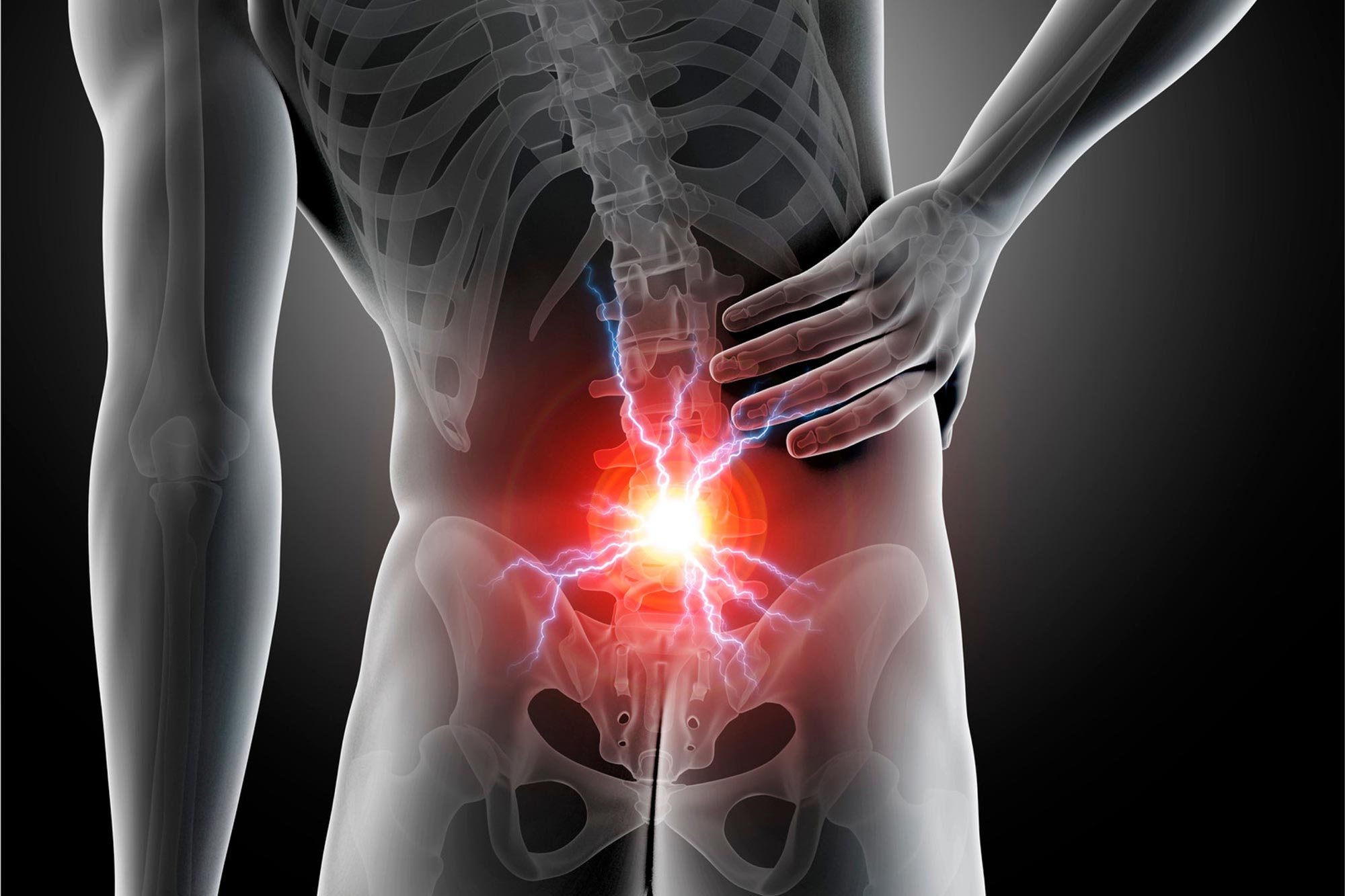
Acute low back pain is a prevalent disability, and an analysis in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research reviewed which non-opioid drugs are most effective in treating this condition. The analysis, which included 18 studies with 3,478 patients, found that muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) can efficiently and quickly alleviate symptoms.
Acute low back pain is a common cause of disability. An analysis in the Journal of Orthopaedic Research examined which non-opioid drugs are best for treating this condition.
The analysis, which included all randomized controlled trials published to date (18 studies with 3,478 patients), showed that muscle relaxants and non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) could effectively and rapidly reduce symptoms.
The combination of NSAIDs and acetaminophen (also known as paracetamol) was associated with a greater improvement than NSAIDs alone.
NSAIDs, which are medicines that are widely used to relieve pain, decrease inflammation, and reduce high temperatures, include the over-the-counter medications ibuprofen, aspirin, and naproxen. These are sold under popular brand names including Advil, Motrin, Bayer, and Aleve. Tylenol is the most common brand name for acetaminophen.
“This is a first step towards the optimization of the management of acute low back pain. However, specific patient characteristics such as having allergies and comorbidities must always be taken into consideration,” said lead author Alice Baroncini, MD, PhD, of RWTH University Hospital in Germany. “Further research will need to focus on the identification of the type of drugs that not only offer the best and quickest pain relief, but also show the lowest rate of symptom recurrence.”
Reference: “Nonopioid pharmacological management of acute low backpain: A level I of evidence systematic review” 22 February 2023, Journal of Orthopaedic Research.
DOI: 10.1002/jor.25508

