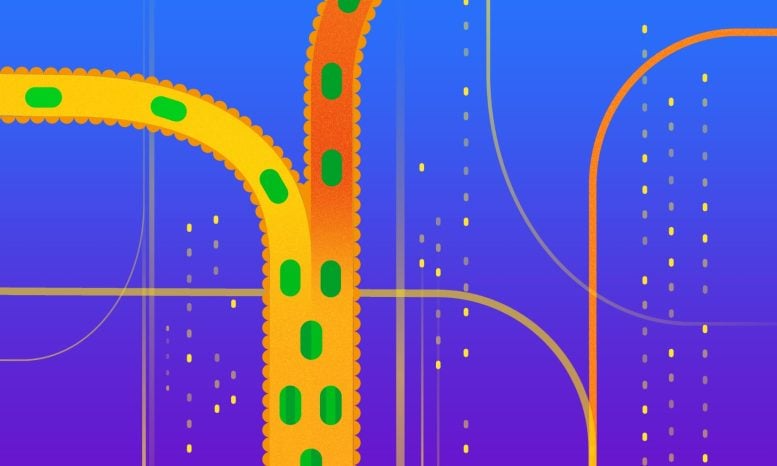
Fecal Microbiota Transplantation as the confluence of a donor’s and recipient’s gut ecosystems. The various “pipes” in the image represent human gastrointestinal tract and the bacteria within represent the recipient’s and donor’s microbial strain populations (by color) that are pitched against each other. Credit: Aleksandra Krolik / EMBL
Scientists used data from over 300 human fecal microbiota transplants to gain an ecological understanding of what happens when two gut microbiomes clash together.
Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) is the transfer of lower intestinal fluids and microbes from one individual to another. It is sometimes used to treat inflammatory gut diseases, such as ulcerative colitis and bacterial infections. A form of it was first recorded all the way back in 4th century China. However, it was not introduced into Western medicine until the 1950s. It has steadily gained prominence in the last two decades.
A team of scientists led by the Bork group at the European Molecular Biology Laboratory (EMBL) Heidelberg, along with their collaborators in the Netherlands and Australia, has now used this unusual medical procedure to ask a fascinating question – what happens when two gut microbiomes mix together?
The answer could hold clues to better therapeutic strategies for gut disorders. It could also provide a richer understanding of how microbial species behave and interact in complex natural ecosystems.
Transplanting microbes
Even though clinical trials have established that FMTs can effectively treat certain gut disorders, their mode of action still remains unclear. Some researchers hypothesize that the gut microbiomes of donors have beneficial properties that help return the recipient’s gut to a healthy state. However, this has never been systematically investigated.
“The ‘super donor’ hypothesis is widely held among practitioners: it postulates that finding ‘good’ donors is essential to the clinical success of an FMT and that a good donor will work for many different patients,” said Sebastian Schmidt. He is one of the first authors of a new study published today (September 15, 2022) in Nature Medicine.
Using clinical and metagenomics data from over 300 FMTs, the scientists discovered, however, that it’s probably the recipient and not the donor that primarily determines the microbial mix resulting from this procedure. This builds upon a 2016 study from the Bork group that demonstrated that microbial strains from a donor can coexist with those from a recipient with metabolic syndrome.
A machine-learning approach was developed by the team to dissect the factors that determine microbial dynamics after an FMT, including the presence or absence of individual microbial species. Their findings show that species richness (a measure of how diverse a recipient’s gut microbiome was before transplant), as well as how different a recipient’s gut microbiome is from a donor’s, are both major factors in determining which species will survive and thrive after a transplant.
An ecological experiment
Simone Li, another first author of this and the 2016 study, finds their results intriguing from an ecological perspective. “Being able to thrive and survive in an entirely new setting is no simple task, especially in a dynamic environment such as the human gastrointestinal tract, where there are constant changes in acidity, oxygen levels, and nutrients, among others,” she said. “As we move towards safer options of microbiome-based therapeutics, what goes in only matters as much as whether they stay long enough to deliver the intended benefits.”
If the researchers treat FMT procedures as ecological experiments where whole microbial ecosystems are supplanted to new locations with pre-existing ecosystems, they could draw important conclusions about which factors help decide how well or easily bacteria can ‘colonize’ in new environments.
This may also have important practical applications, as Peer Bork, the corresponding author of the study, points out. “As our understanding of the ecological processes in the gut following FMT improves, we may discover more precise and more targeted links to clinical effects – for example, to displace only specific strains (e.g. pathogens) while minimizing ‘collateral’ effects to the rest of the microbiome.”
Although the study dealt primarily with bacteria and archaea, which together make up over 90 % of the gut microbiome, the scientists expect that future research may also incorporate data from fungi, other eukaryotes, and viruses to obtain a more holistic view of this process.
“I hope (and am confident) that our findings will help to design more efficacious FMT protocols in the future. We provide data on which parameters are worth tuning (and which are not) when you aim to modulate the recipient’s microbiome. On a longer term, this may also inform the design of ’next-gen’ personalized probiotic treatments,” Schmidt said.
Reference: “Drivers and Determinants of Strain Dynamics Following Fecal Microbiota Transplantation” 15 September 2022, Nature Medicine.
DOI: 10.1038/s41591-022-01913-0