The study demonstrated that the reproductive system influences overall health and aging.
The study identified the negative consequences of disrupting meiosis.
A new study in an animal model of aging indicates a potential reason for why women who have early menopause or other genetic conditions affecting the reproductive system are more prone to develop cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and dementia.
The new study, led by researchers from the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC and published in the journal Aging Cell, found that disrupting a process called meiosis in C. elegans reproductive cells caused a decline in the worms’ health and triggered an accelerated aging gene signature similar to that of aging humans.
“This study is exciting because it’s the first direct evidence that manipulating the health of reproductive cells leads to premature aging and a decline in healthspan,” said senior author Arjumand Ghazi, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics, developmental biology, and cell biology and physiology at Pitt and UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. “The implications of this finding are profound: It suggests that the status of the reproductive system is important not simply to produce children, but also for overall health.”
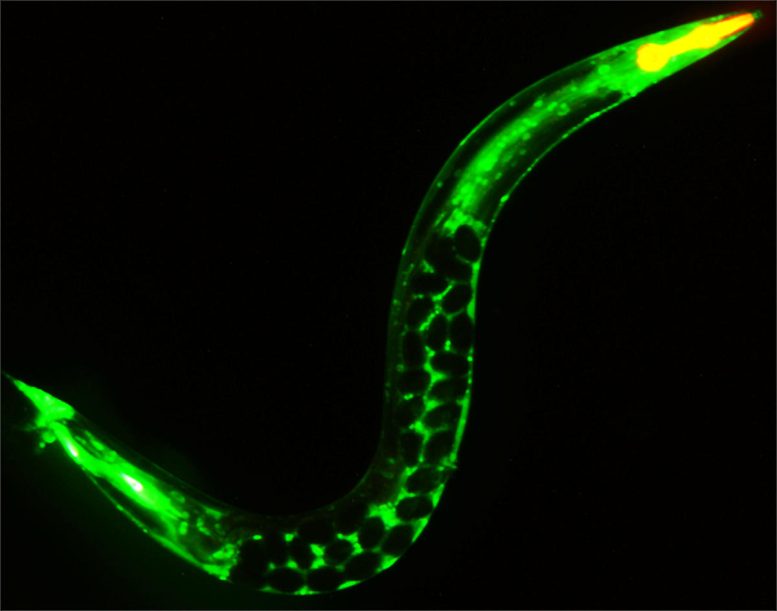
A young C. elegans adult glowing green where a protein has been linked to a fluorescent tag and filled with soon-to-be-laid eggs that appear as dark spheres in the mother’s body. Disruption of meiosis, a process on which the creation of these eggs depends, shortens the animal’s entire lifespan and accelerates its aging. Credit: Scott Keith & Arjumand Ghazi
While the consequences of aging on fertility are well known, research in the past two decades has started to show that reproductive fitness also has an impact on human aging and health. The issue is that it is difficult to directly examine this kind of cause and effect in humans. Ghazi and her colleagues then turned to the Caenorhabditis elegans, a microscopic nematode worm that is an ideal system for aging research due to its short lifetime (three weeks from birth to death) and shared genetic pathways with humans.
Arjumand Ghazi, Ph.D., associate professor of pediatrics, developmental biology, and cell biology and physiology at the University of Pittsburgh and UPMC Children’s Hospital of Pittsburgh. Credit: UPMC
The researchers studied meiosis, a kind of cell division present in all animals from yeast to humans that happens exclusively in cells destined to produce sperm or eggs. They discovered that animals with mutations in meiosis genes had shorter lives than their non-mutated counterparts. The mutants also had worse overall health ratings, including premature reductions in mobility, muscular function, and memory.
“The exciting part of this healthspan work was that these animals also showed signs of disrupted protein homeostasis,” said Ghazi. “Disruption to the balance of proteins inside cells is at the heart of age-related neurodegenerative diseases, like DOI: 10.1111/acel.13716
The study was funded by the National Institutes of Health.