Bargaining —
Much of the drugs’ costs are due to repeated price hikes over the years.
Beth Mole
–
The first 10 prescription drugs up for Medicare price negotiations have had years of price hikes that have ratcheted up costs for US taxpayers—which totaled $50.5 billion in gross Medicare Part D coverage costs in the past year and $3.4 billion in out-of-pocket costs in 2022.
Today, the Department of Health and Human Services announced the 10 drugs selected for the first round of Medicare price negotiations, established under the Inflation Reduction Act. All but one of the announced drugs were among the top 25 costliest Medicare Part D prescriptions in 2021. An analysis by the AARP released earlier this month found that those top 25 drugs had price increases that, on average, tripled their list prices in their time on the market and far exceeded the rate of inflation.
The 10 selected today were no exception. The drugs are used by about 9 million Medicare Part D enrollees and treat various conditions, from diabetes, psoriasis, blood clots, heart failure, chronic kidney disease, to blood cancers. Based on 2021 prices, the nine drugs included in the AARP analysis were found to have list price increases averaging 262 percent in their time on the market. The average corresponding rate of inflation for the nine drugs was 64 percent.
The one drug that was not found in the top 25 costliest drugs in 2021 was Farxiga, a drug used to treat diabetes, heart failure, and chronic kidney disease. Although the drug was released in 2014 to treat type II diabetes, its maker, AstraZeneca, received further approvals in recent years to bolster the drug’s use. In 2019, the Food and Drug Administration approved its use for heart failure, and in 2021, the agency approved its use for chronic kidney disease. According to the most up-to-date data released today by the Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS), nearly 800,000 Medicare Part D enrollees used the drug between June 2022 and May 2023. In that time, Part D coverage for the drug totaled nearly $3.3 billion. A separate data report released from the HHS today found that the average out-of-pocket costs for enrollees was $260 in the calendar year of 2022.
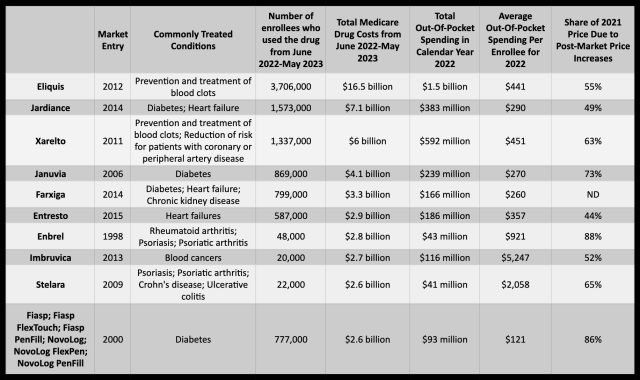
Enlarge / Table showing data from HHS, CMS, and AARP on the 10 drugs selected for negotiations.
That is far from the costliest drug on the list. Eliquis, a drug for blood clots that hit the market in 2012, easily took the top ranking. From June 2022 to May 2023, Medicare Part D gross coverage costs for Eliquis reached $16.5 billion to supply the drug to 3.7 million enrollees. During 2022, total out-of-pocket spending for the medication reached $1.5 billion, with out-of-pocket costs per enrollee averaging $441. In the AARP analysis, Eliquis—sold by Bristol Myers Squibb and Pfizer—had a list price increase of 124 percent between 2012 and 2021, while inflation during that time was 31 percent.
The drug on the list with the highest post-market price increase was Enbrel, an arthritis and psoriasis drug by Amgen that hit the market in 1998. Between 1998 and 2021, the drug’s list price increased 701 percent, while the rate of inflation over that period was 85 percent. In 2021, 88 percent of Enbrel’s list price was due to post-market price hikes. Those price hikes come across in the latest data from the HHS. Between June 2022 and May 2023, Medicare Part D gross coverage costs reached $2.8 billion for Enbrel, despite only 48,000 enrollees using it during that time. In 2022, out-of-pocket spending reached $43 million, with the average out-of-pocket costs per enrollee at $921.



![PURE JOY! Husband and Toddler Daughter Greet Pro-Life Street Preacher Bevelyn Williams After She’s Released From Prison, Thanks To Trump Pardon [VIDEO]](https://www.thegatewaypundit.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/bevelyn-beatty-williams-1200x630.jpg)